Sunday, January 28, 2007
Wednesday, January 17, 2007
SQL Server Optimization Tips for Designing Tables(ZT)
-
Normalize your tables to the third normal form.
A table is in third normal form (3NF) if it is in second normal form (2NF) and if it does not contain transitive dependencies. In most cases, you should normalize your tables to the third normal form. The normalization is used to reduce the total amount of redundant data in the database. The less data there is, the less work SQL Server has to perform, speeding its performance. -
Consider the denormalization of your tables from the forth or fifth normal forms to the third normal form.
Normalization to the forth and fifth normal forms can result in some performance degradation, especially when you need to perform many joins against several tables. It may be necessary to denormalize your tables to prevent performance degradation. -
Consider horizontal partitioning of the very large tables into the current and the archives versions.
The less space used, the smaller the table, the less work SQL Server has to perform to evaluate your queries. For example, if you need to query only data for the current year in your daily work, and you need all the data only once per month for the monthly report, you can create two tables: one with the current year's data and one with the old data. -
Create the table's columns as narrow as possible.
This can reduce the table's size and improve performance of your queries as well as some maintenance tasks (such as backup, restore and so on). -
Try to reduce the number of columns in a table.
The fewer the number of columns in a table, the less space the table will use, since more rows will fit on a single data page, and less I/O overhead will be required to access the table's data. -
Try to use constraints instead of triggers, rules, and defaults whenever possible.
Constraints are much more efficient than triggers and can boost performance. Constraints are more consistent and reliable in comparison to triggers, rules and defaults, because you can make errors when you write your own code to perform the same actions as the constraints. -
If you need to store integer data from 0 through 255, use tinyint data type.
The columns with tinyint data type use only one byte to store their values, in comparison with two bytes, four bytes and eight bytes used to store the columns with smallint, int and bigint data types accordingly. For example, if you design tables for a small company with 5-7 departments, you can create the departments table with the DepartmentID tinyint column to store the unique number of each department. -
If you need to store integer data from -32,768 through 32,767, use smallint data type.
The columns with smallint data type use only two bytes to store their values, in comparison with four bytes and eight bytes used to store the columns with int and bigint data types respectively. For example, if you design tables for a company with several hundred employees, you can create an employee table with the EmployeeID smallint column to store the unique number of each employee. -
If you need to store integer data from -2,147,483,648 through 2,147,483,647, Use int data type.
The columns with int data type use only four bytes to store their values, in comparison with eight bytes used to store the columns with bigint data types. For example, to design tables for a library with more than 32,767 books, create a books table with a BookID int column to store the unique number of each book. -
Use smallmoney data type instead of money data type, if you need to store monetary data values from 214,748.3648 through 214,748.3647.
The columns with smallmoney data type use only four bytes to store their values, in comparison with eight bytes used to store the columns with money data types. For example, if you need to store the monthly employee payments, it might be possible to use a column with the smallmoney data type instead of money data type. -
Use smalldatetime data type instead of datetime data type, if you need to store the date and time data from January 1, 1900 through June 6, 2079, with accuracy to the minute.
The columns with smalldatetime data type use only four bytes to store their values, in comparison with eight bytes used to store the columns with datetime data types. For example, if you need to store the employee's hire date, you can use column with the smalldatetime data type instead of datetime data type. -
Use varchar/nvarchar columns instead of text/ntext columns whenever possible.
Because SQL Server stores text/ntext columns on the Text/Image pages separately from the other data, stored on the Data pages, it can take more time to get the text/ntext values. -
Use char/varchar columns instead of nchar/nvarchar if you do not need to store unicode data.
The char/varchar value uses only one byte to store one character, the nchar/nvarchar value uses two bytes to store one character, so the char/varchar columns use two times less space to store data in comparison with nchar/nvarchar columns. -
Consider setting the 'text in row' SQL Server 2000 table's option.
The text, ntext, and image values are stored on the Text/Image pages, by default. This option specifies that small text, ntext, and image values will be placed on the Data pages with other data values in a data row. This can increase the speed of read and write operations and reduce the amount of space used to store small text, ntext, and image data values. You can set the 'text in row' table option by using the sp_tableoption stored procedure. -
If you work with SQL Server 2000, use cascading referential integrity constraints instead of triggers whenever possible.
For example, if you need to make cascading deletes or updates, specify the ON DELETE or ON UPDATE clause in the REFERENCES clause of the CREATE TABLE or ALTER TABLE statements. The cascading referential integrity constraints are much more efficient than triggers and can boost performance
Saturday, January 06, 2007
(ZT)Asp.net与SQL一起打包部署安装
借鉴msdn webcasts的Asp.net程序部署和李洪根的一篇文章,然后加上自己的亲身体会,把整个SQL和Asp.net(vb.net)一起打包的全过程写一下。
一.准备必要的文件
1. SQL脚本文件,生成以后安装过程中需要的表和存储过程等等;
生成之后,就暂时把它命名为db.sql(注意大小写)
2.LisenceFile.rtf的安装文件,因为我的系统是个人的,而且free的,所以就没有做。这个以后也是要用到的。
二.在自己现有的项目里面创建部署项目:
1. 在“文件”菜单上指向“添加项目”,然后选择“新建项目”。(图1-2)
2. 在“添加新项目”对话框中,选择“项目类型”窗格中的“安装和部署项目”,然后选择“模板”窗格中的“Web 安装项目”。在“名称”框中键入 Test Installer。(图1-3)
3. 单击“确定”关闭对话框。
4. 项目被添加到解决方案资源管理器中,并且文件系统编辑器打开。
5. 在“属性”窗口中,选择 ProductName 属性,并键入 GCRM。 
(1-2)
(图1-3)其他项目的作用可以参考Webcast
三。将 VbNetTest项目的输出添加到部署项目中(假如你的虚拟目录是SQLANDASPNet)
1. 在“文件系统编辑器”中,选择“Web 应用程序文件夹"。在“操作”菜单上,指向“添加”,然后选择“项目输出”。(图1-4)
2. 在“添加项目输出组”对话框中,选择“项目”下拉列表中的“SQLANDASPNet”。
3. 单击“确定”关闭对话框。
4. 从列表中选择“主输出”和“内容文件”组,然后单击“确定”。(图1-5)
(图1-4)
(图1-5)其他的作用可以参考webcast,源文件就是所有项目的的文件
四.
创建自定义安装对话框
1. 在解决方案资源管理器中选择“Test Installer”项目。在“视图”菜单上指向“编辑器”,然后选择“用户界面”。 (图1-6)
2. 在用户界面编辑器中,选择“安装”下的“启动”节点。在“操作”菜单上,选择“添加对话框”。
3. 在“添加对话框”对话框中,选择“许可协议”对话框,然后单击“确定”关闭对话框。 (注:我没有添加,因为暂时我还是不需要,需要的要添加一下哦)
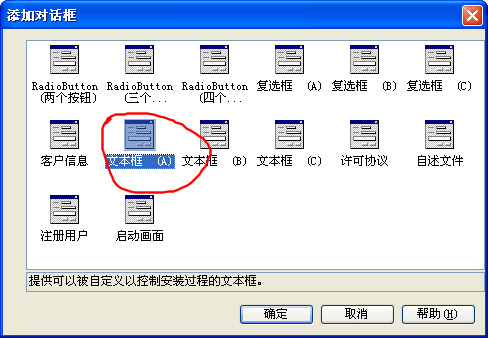
4. 在“添加对话框”对话框中,选择“文本框 (A)”对话框,然后单击“确定”关闭对话框。 (图1-7)
5. 在“操作”菜单上,选择“上移”。重复此步骤,直到“文本框 (A)”对话框位于“安装文件夹”节点之上。
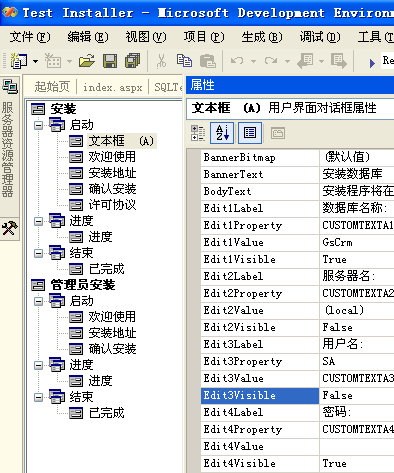
6. 在“属性”窗口中,选择 BannerText 属性并键入:安装数据库.。
7. 选择 BodyText 属性并键入:安装程序将在目标机器上安装数据库。
8. 选择 Edit1Label 属性并键入:数据库名称:。
9. 选择 Edit1Property 属性并键入 CUSTOMTEXTA1。
10. 选择 Edit1Value 属性并键入:GsCrm。
11. 选择 Edit2Label 属性并键入:服务器名:。
12. 选择 Edit2Property 属性并键入 CUSTOMTEXTA2。
13. 选择 Edit2Value 属性并键入:(local)。
14. 选择 Edit3Label 属性并键入:用户名:。
15. 选择 Edit3Value 属性并键入:sa。
16. 选择 Edit3Property 属性并键入 CUSTOMTEXTA3。
17. 选择 Edit4Label 属性并键入:密码:。
18. 选择 Edit4Property 属性并键入 CUSTOMTEXTA4。
19. 选择 Edit2Visible、Edit3Visible ,并将它们设置为 False。(图1-8)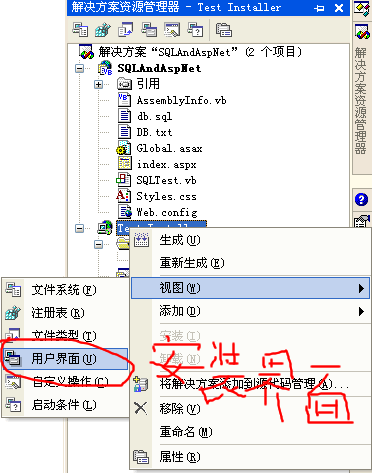
(图1-7)
(图1-8)
(五).创建自定义操作
1. 在解决方案资源管理器中选择“Test Installer”项目。在“视图”菜单上指向“编辑器”,然后选择“自定义操作”。(图1-9)
2. 在自定义操作编辑器中选择“安装”节点。在“操作”菜单上,选择“添加自定义操作”。
3. 在“选择项目中的项”对话框中,双击“应用程序文件夹”。
4. 选择“主输出来自 DBCustomAction(活动)”项,然后单击“确定”关闭对话框。
5. 在“属性”窗口中,选择 CustomActionData 属性并键入 /dbname=[CUSTOMTEXTA1] /server=[CUSTOMTEXTA2] /user=[CUSTOMTEXTA3] /pwd=[CUSTOMTEXTA4] /targetdir="[TARGETDIR]\"。 (图1-10)
附/targetdir="[targetdir]\"是安装后的目标路径,为了在dbcustomaction类中获得安装后的路径,我们设置此参数。
另外,安装后的路径也可以通过Reflection得到:
Dim Asm As System.Reflection.Assembly = _
System.Reflection.Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly
MsgBox("Asm.Location")
(图1-9)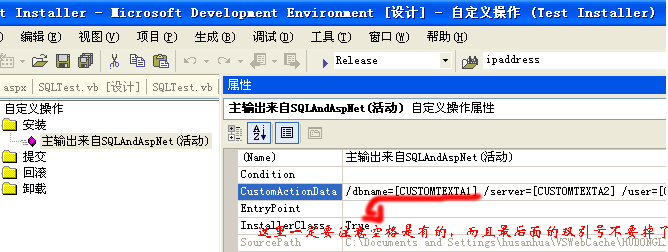
(图1-10)
呵呵,已经好多了,剩下来的是关键性步骤,我花了好多时间研究。
(六)创建安装程序类
1. 在“文件”菜单上指向“新建”,然后选择“项目”。
2. 在“新建项目”对话框中,选择“项目类型”窗格中的“Visual Basic 项目”,然后选择“模板”窗格中的“类库”。在“名称”框中键入 DBCustomAction。
3. 单击“打开”关闭对话框。
4. 从“项目”菜单中选择“添加新项”。
5. 在“添加新项”对话框中选择“安装程序类”。在“名称”框中键入 DBCustomAction。
6. 单击“确定”关闭对话框。(图1-11,1-12)
注:这里是在原来的项目上建立一个简单的安装文件就可以了。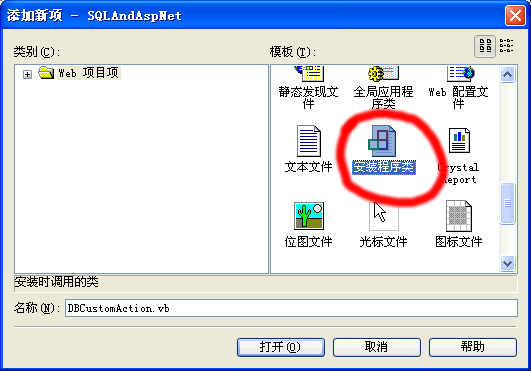
(图1-11)
添加后的效果图: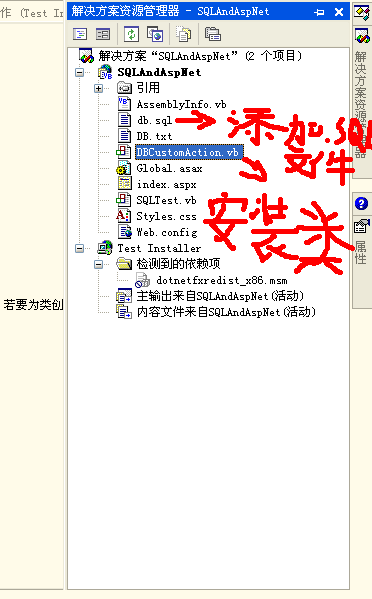
(图1-12)这里的sql文件是要等一下添加的
(七)
添加文件
1. 将SQL Server生成的脚本文件db.sql添加到“Test Installer”项目(图1-12)
2. 将安装文件LisenceFile.rtf添加到“Test Installer”项目
3. 在用户界面编辑器中,选择许可协议,设置LisenceFile属性为LisenceFile.rtf文件
(八)
一下的代码是整个部署的最重要的一部分了
将代码添加到安装程序类中,dbcustomaction.vb类
Imports System.ComponentModel
imports System.Configuration.Install
imports System.IO
imports System.Reflection
Public Class DBCustomActionClass DBCustomAction
inherits System.Configuration.Install.Installer
组件设计器生成的代码#region "组件设计器生成的代码 "
public Sub New()Sub New()
mybase.new()
'该调用是组件设计器所必需的
initializecomponent()
'在 InitializeComponent() 调用之后添加任何初始化
end Sub
' Installer 重写 dispose 以清理组件列表。
protected Overloads Overrides Sub Dispose()Sub Dispose(ByVal disposing As Boolean)
if disposing Then
if Not (components Is Nothing) Then
components.dispose()
end If
end If
mybase.dispose(disposing)
end Sub
private components As System.ComponentModel.IContainer
Private Sub InitializeComponent()Sub InitializeComponent()
end Sub
#end Region
'执行sql 语句
private Sub ExecuteSql()Sub ExecuteSql(ByVal conn As String, ByVal DatabaseName As String, ByVal Sql As String)
dim mySqlConnection As New SqlClient.SqlConnection(conn)
dim Command As New SqlClient.SqlCommand(Sql, mySqlConnection)
command.connection.open()
command.connection.changedatabase(databasename)
try
command.executenonquery()
finally
'close Connection
command.connection.close()
end Try
end Sub
public Overrides Sub Install()Sub Install(ByVal stateSaver As System.Collections.IDictionary)
MyBase.Install(stateSaver)
' ------------------------建立数据库-------------------------------------------------
try
dim connStr As String = String.Format("data source={0};user id={1};password={2};persist security info=false;packet size=4096", Me.Context.Parameters.Item("server"), Me.Context.Parameters.Item("user"), Me.Context.Parameters.Item("pwd"))
'根据输入的数据库名称建立数据库
executesql(connstr, "master", "CREATE DATABASE " + Me.Context.Parameters.Item("dbname"))
'调用osql执行脚本
dim sqlProcess As New System.Diagnostics.Process
sqlprocess.startinfo.filename = "osql.exe "
sqlprocess.startinfo.arguments = String.Format(" -U {0} -P {1} -d {2} -i {3}db.sql", Me.Context.Parameters.Item("user"), Me.Context.Parameters.Item("pwd"), Me.Context.Parameters.Item("dbname"), Me.Context.Parameters.Item("targetdir"))
sqlprocess.startinfo.windowstyle = ProcessWindowStyle.Hidden
sqlprocess.start()
sqlprocess.waitforexit() '等待执行
sqlprocess.close()
'删除脚本文件
dim sqlFileInfo As New System.IO.FileInfo(String.Format("{0}db.sql", Me.Context.Parameters.Item("targetdir")))
if sqlFileInfo.Exists Then
sqlfileinfo.delete()
end If
catch ex As Exception
throw ex
end Try
' ---------------------将连接字符串写入Web.config-----------------------------------
try
dim FileInfo As System.IO.FileInfo = New System.IO.FileInfo(Me.Context.Parameters.Item("targetdir") & "\web.config")
if Not FileInfo.Exists Then
throw New InstallException("没有找到配置文件")
end If
'实例化xml文档
dim XmlDocument As New System.Xml.XmlDocument
xmldocument.load(fileinfo.fullname)
'查找到appsettings中的节点
dim Node As System.Xml.XmlNode
dim FoundIt As Boolean = False
for Each Node In XmlDocument.Item("configuration").Item("appSettings")
if Node.Name = "add" Then
if Node.Attributes.GetNamedItem("key").Value = "connString" Then
'写入连接字符串
node.attributes.getnameditem("value").value = String.Format("Persist Security Info=False;Data Source={0};Initial Catalog={1};User ID={2};Password={3};Packet Size=4096;Pooling=true;Max Pool Size=100;Min Pool Size=1", _
me.context.parameters.item("server"), Me.Context.Parameters.Item("dbname"), Me.Context.Parameters.Item("user"), Me.Context.Parameters.Item("pwd"))
foundit = True
end If
end If
next Node
if Not FoundIt Then
throw New InstallException("web.Config 文件没有包含connString连接字符串设置")
end If
xmldocument.save(fileinfo.fullname)
catch ex As Exception
throw ex
end Try
end Sub
end Class
有点难度的就是那个process类,它调用了osql.exe程序,来执行sql语句osql -U,-P,,-d,-i。
web.config的修改代码是利用xml的语法实现。不是很难理解。
最后编译生成!如图:
安装界面:如图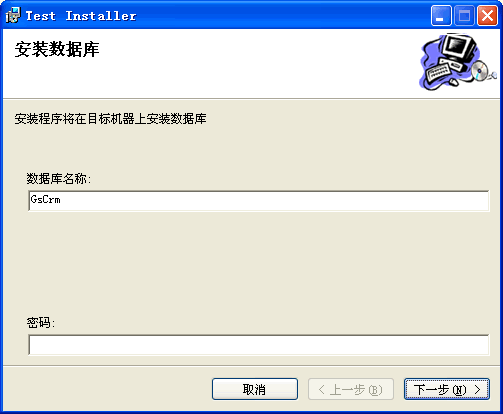
哈哈,总算写完了,也不知道有没有写好![]() 。
。
最后还是感谢李洪根老师和微软的讲师。结合他们的共同的经验,部署起来真的很简单。
 -->
-->
